Glucose metabolism is an essential process that keeps our bodies running. It’s how the food we eat gets converted into energy that fuels everything we do, from thinking and breathing to running a marathon. But how does this process work, and why is it so important? In this blog, we’ll explore the fascinating world of glucose metabolism, its impact on your health, and what happens when things go wrong.
What is Glucose Metabolism?
Glucose metabolism refers to the series of biochemical reactions where glucose, a simple sugar, is broken down to produce energy. Every cell in your body relies on glucose as its primary energy source. This process involves the digestive, circulatory, and endocrine systems working together to ensure glucose is delivered to cells and used efficiently.
When you eat carbohydrates, your body breaks them down into glucose. This glucose enters your bloodstream, raising your blood sugar levels. In response, your pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps transport glucose into cells for energy. This delicate balance is crucial for maintaining overall health.
The Key Steps of Glucose Metabolism
Glycolysis
The first step in glucose metabolism is glycolysis. This occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and breaks one molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP (energy) and NADH (an electron carrier).
Pyruvate Oxidation
Pyruvate is then transported to the mitochondria, where it is further processed to produce acetyl-CoA, a key molecule in energy production.
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
In the mitochondria, acetyl-CoA enters the Krebs cycle, generating even more ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
The final step involves the electron transport chain. Here, NADH and FADH2 donate electrons, creating a flow that produces a large amount of ATP.
This entire sequence of reactions highlights the complexity and efficiency of glucose metabolism in energy production.

Why is Glucose Metabolism Important?
Glucose metabolism is essential because it provides the energy our bodies need to function. From contracting muscles to powering brain cells, every system relies on the ATP generated through this process. Additionally, glucose metabolism plays a significant role in maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
When glucose metabolism functions properly, blood sugar remains within a healthy range. However, when this process is impaired, it can lead to metabolic disorders like diabetes, obesity, and insulin resistance.
Factors That Affect Glucose Metabolism
Several factors influence how efficiently your body metabolizes glucose:
- Diet: Consuming excessive sugar and refined carbs can overwhelm the body’s ability to manage glucose, leading to insulin resistance.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to absorb glucose more effectively.
- Hormonal Balance: Hormones like insulin, and cortisol regulate glucose metabolism.
- Genetics: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to insulin resistance or metabolic syndrome.
Glucose Metabolism and Health Conditions
1. Diabetes: When glucose metabolism malfunctions, it often results in diabetes. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells, while Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance.
2. Obesity: Impaired glucose metabolism can lead to excess glucose being stored as fat, contributing to weight gain and obesity.
3. Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia: Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) and high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) are both symptoms of disrupted glucose metabolism.

How to Support Healthy Glucose Metabolism?
Supporting your glucose metabolism is key to maintaining energy levels and preventing disease. Here are some tips to optimize this process:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on complex carbohydrates, fiber, and healthy fats.
- Stay Active: Incorporate both aerobic exercise and strength training into your routine.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can interfere with glucose metabolism by increasing cortisol levels.
- Get Enough Sleep: Quality sleep helps regulate hormones involved in glucose metabolism.
Enhance Your Glucose Metabolism with Gaspari Nutrition Proven GDA
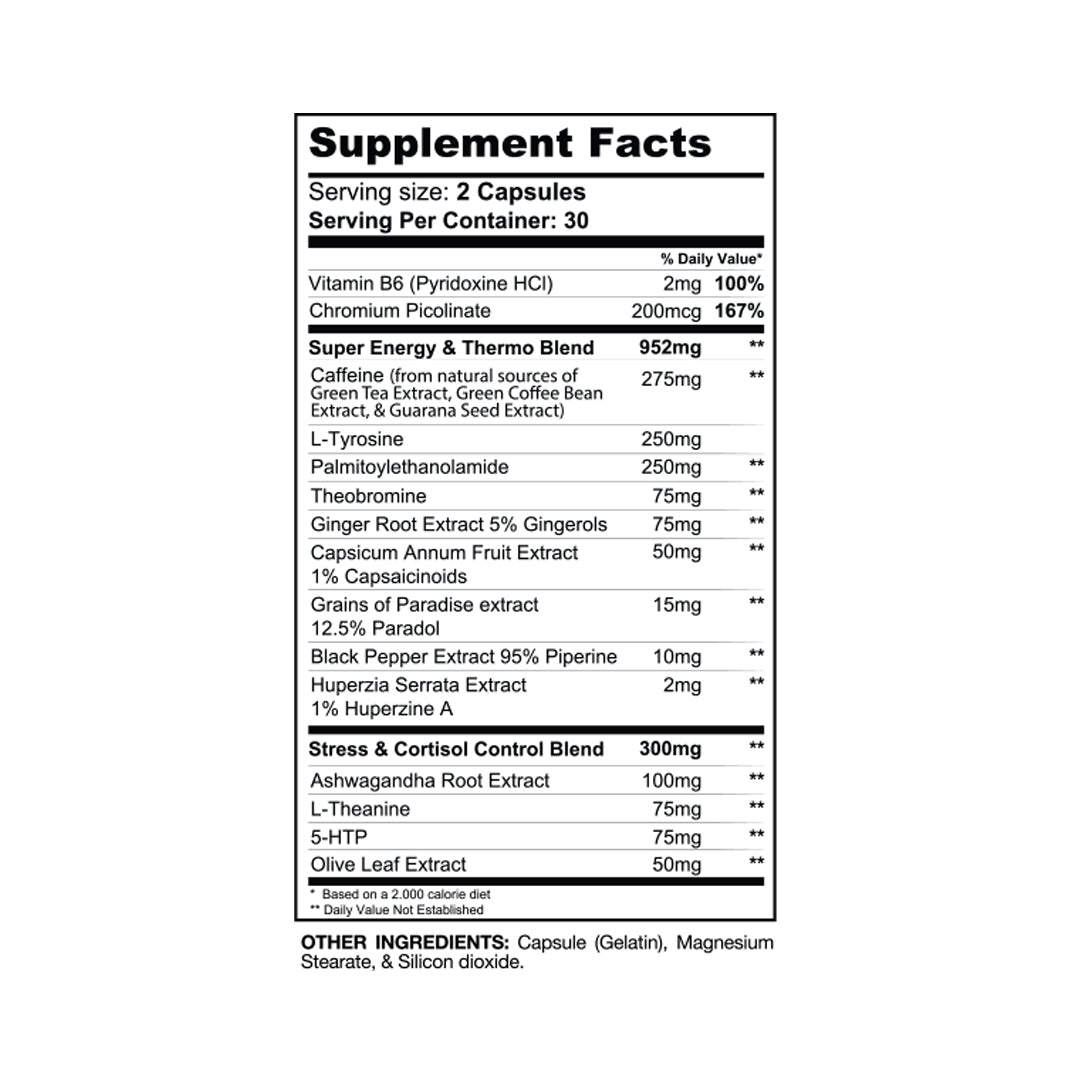
For those looking to further support their glucose metabolism, Gaspari Nutrition Proven GDA (Glucose Disposal Agent) can be a valuable addition. This supplement is designed to help your body efficiently manage glucose by driving it into your muscles rather than storing it as fat.
It contains powerful ingredients that enhance insulin sensitivity and optimize nutrient uptake. Whether you're an athlete seeking better performance or simply aiming for balanced blood sugar levels, incorporating a quality glucose disposal agent like Proven GDA can make a significant difference.
Final Thoughts
Glucose metabolism is a remarkable and intricate process that sustains life by converting food into energy. By understanding how it works and taking proactive steps to support it, you can improve your energy levels, maintain a healthy weight, and reduce your risk of metabolic disorders.
Remember, small lifestyle changes can make a big difference in how your body handles glucose. So, take charge of your health by nourishing your body, moving more, and managing stress. Your glucose metabolism will thank you!
If you have concerns about your glucose metabolism or experience symptoms like fatigue, excessive thirst, or frequent urination, consider speaking with a healthcare provider for further evaluation.











































































Share:
How Do I Start Intermittent Fasting? A Beginner's Guide
Muscle Recovery Supplements: The Secret to Faster Gains